Among the most pressing issues for the global steel industry is the need to reduce its environmental footprint. With air pollution control regulations becoming stricter worldwide, steel producers are required to measure and control emissions of harmful gases during the steelmaking process and downstream operations.
Additionally, public awareness of climate change has intensified, leading to increased pressure on supply chains to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Fortunately, there are technologies available that can enhance combustion efficiency and minimise pollution emissions. This article will focus on two measurement techniques that can significantly improve the efficiency of reheat furnaces in rolling processes.

One crucial aspect of improving furnace operation is optimising temperature distribution within the reheat furnace. AMETEK Land offers
NIR-B and MWIR-B infrared borescope imagers, which provide radiometric thermal images and videos inside the furnace. These systems allow furnace operators to monitor stock or billet temperatures and optimise the air-fuel ratio, resulting in reduced emissions of toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Moreover, this optimisation leads to lower fuel consumption, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and improved product quality.
Thermocouples and single-point infrared thermometers have traditionally been used to measure temperatures in furnaces. However, these methods have limitations. Thermocouples measure furnace walls and atmosphere temperatures but not the billet itself, necessitating the use of mathematical models to estimate billet temperature. This often leads to conservative estimates, resulting in overheating and wasted fuel. On the other hand, single-point infrared thermometers can measure billet temperature but are susceptible to significant errors due to reflections from the billet surface.
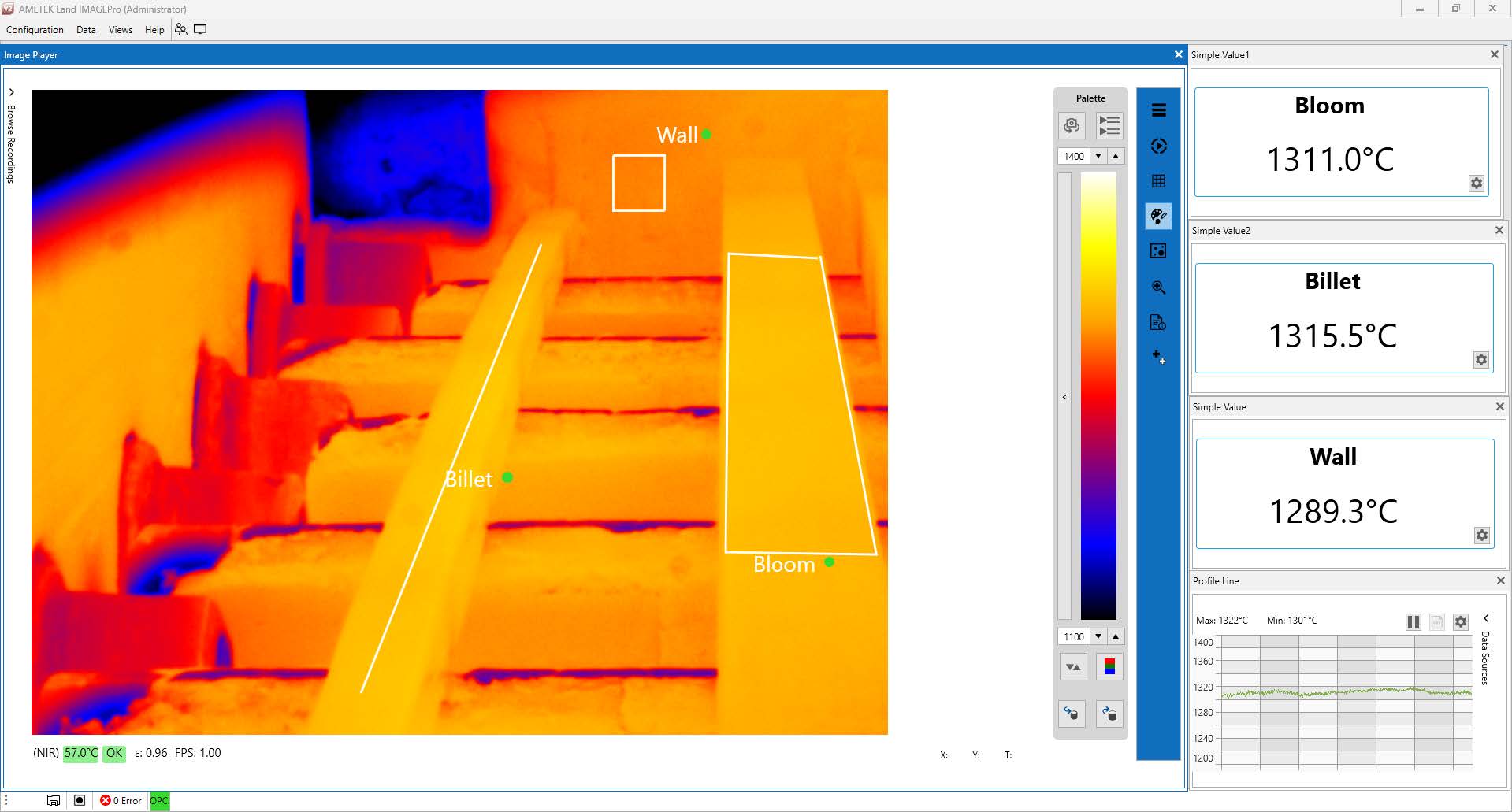
Furnace thermal imaging systems overcome the limitations of traditional temperature measurement techniques. These systems use borescope cameras with lenses that form wide-angle images, allowing the sensitive electronics to be located outside the furnace while capturing images of the interior.
AMETEK Land's
near- and mid-wavelength infrared borescopes provide radiometric images with accurate temperature measurement points, comparable to conventional spot pyrometers. The borescope lenses are protected by water-cooled and air-purged housings, and an automatic retraction system withdraws the borescope if necessary. The accompanying
IMAGEPro image processing software enables temperature measurement and display at any point in the image, including billets, walls, ceiling, and rollers.
Another vital aspect of reducing emissions and improving efficiency is optimising the fuel/air ratio inside the furnace. While stoichiometric combustion under ideal conditions would result in complete fuel and oxygen consumption, real furnaces rarely achieve this state. Therefore, the exhaust gases contain residual oxygen (O2) and carbon monoxide (CO) alongside carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapour (H2O). Loss mechanisms, such as fuel-rich conditions or excessive air, contribute to inefficient combustion. By measuring oxygen and carbon monoxide levels, precise control of the fuel/air ratio can be achieved, resulting in improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions.
 AMETEK Land
AMETEK Land offers the
FGA 930E and FGA 950E gas analyzers, which provide accurate measurements of carbon monoxide (CO) and oxygen (O2) concentrations in the furnace. The FGA 930E is a fully extractive system that includes sample conditioning and analysis, while the FGA 950E adds an NO sensor to optimise combustion and minimise nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions. These analyzers enable precise control of the combustion process, leading to enhanced efficiency and reduced pollutant emissions.
In conclusion, reducing emissions and improving combustion efficiency in reheating furnaces is a critical step in addressing environmental concerns in the steel industry.
AMETEK Land's furnace thermal imaging systems provide valuable insights into temperature distribution, allowing operators to optimize furnace operation, reduce toxic gas emissions, lower fuel consumption, and improve product quality.
Additionally, the use of
gas analyzers, such as the FGA 930E and FGA 950E, enables precise control of the fuel/air ratio, resulting in enhanced combustion efficiency and reduced emissions of carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other pollutants. By adopting these technologies, steel producers can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly steelmaking process.
Click here to read the Reducing Emissions & Improving Combustion Efficiency in Reheat Furnaces reference guide.